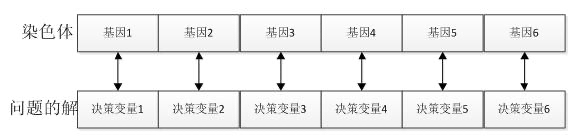
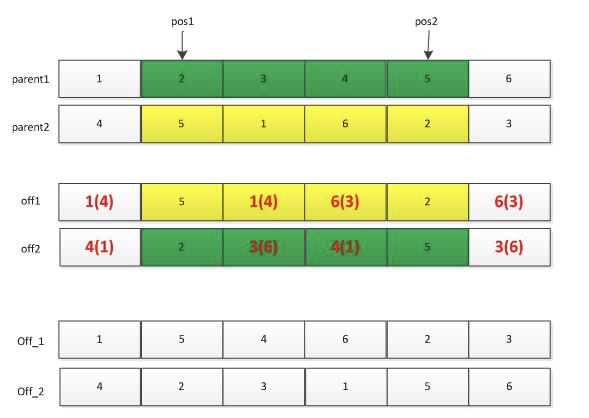
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
|
import numpy as np
from scipy.optimize import fsolve, basinhopping
import random
import timeit
def getEncodedLength(delta=0.0001, boundarylist=[]):
lengths = []
for i in boundarylist:
lower = i[0]
upper = i[1]
res = fsolve(lambda x: ((upper - lower) * 1 / delta) - 2 ** x - 1, 50)
length = int(np.floor(res[0]))
lengths.append(length)
return lengths
def getIntialPopulation(encodelength, populationSize):
chromosomes = np.zeros((populationSize, sum(encodelength)), dtype=np.uint8)
for i in range(populationSize):
chromosomes[i, :] = np.random.randint(0, 2, sum(encodelength))
return chromosomes
def decodedChromosome(encodelength, chromosomes, boundarylist, delta=0.0001):
populations = chromosomes.shape[0]
variables = len(encodelength)
decodedvalues = np.zeros((populations, variables))
for k, chromosome in enumerate(chromosomes):
chromosome = chromosome.tolist()
start = 0
for index, length in enumerate(encodelength):
power = length - 1
demical = 0
for i in range(start, length + start):
demical += chromosome[i] * (2 ** power)
power -= 1
lower = boundarylist[index][0]
upper = boundarylist[index][1]
decodedvalue = lower + demical * (upper - lower) / (2 ** length - 1)
decodedvalues[k, index] = decodedvalue
start = length
return decodedvalues
def getFitnessValue(func, chromosomesdecoded):
population, nums = chromosomesdecoded.shape
fitnessvalues = np.zeros((population, 1))
for i in range(population):
fitnessvalues[i, 0] = func(chromosomesdecoded[i, :])
probability = fitnessvalues / np.sum(fitnessvalues)
cum_probability = np.cumsum(probability)
return fitnessvalues, cum_probability
def selectNewPopulation(chromosomes, cum_probability):
m, n = chromosomes.shape
newpopulation = np.zeros((m, n), dtype=np.uint8)
randoms = np.random.rand(m)
for i, randoma in enumerate(randoms):
logical = cum_probability >= randoma
index = np.where(logical == 1)
newpopulation[i, :] = chromosomes[index[0][0], :]
return newpopulation
def crossover(population, Pc=0.8):
"""
:param population: 新种群
:param Pc: 交叉概率默认是0.8
:return: 交叉后得到的新种群
"""
m, n = population.shape
numbers = np.uint8(m * Pc)
if numbers % 2 != 0:
numbers += 1
updatepopulation = np.zeros((m, n), dtype=np.uint8)
index = random.sample(range(m), numbers)
for i in range(m):
if not index.__contains__(i):
updatepopulation[i, :] = population[i, :]
while len(index) > 0:
a = index.pop()
b = index.pop()
crossoverPoint = random.sample(range(1, n), 1)
crossoverPoint = crossoverPoint[0]
updatepopulation[a, 0:crossoverPoint] = population[a, 0:crossoverPoint]
updatepopulation[a, crossoverPoint:] = population[b, crossoverPoint:]
updatepopulation[b, 0:crossoverPoint] = population[b, 0:crossoverPoint]
updatepopulation[b, crossoverPoint:] = population[a, crossoverPoint:]
return updatepopulation
def mutation(population, Pm=0.01):
"""
:param population: 经交叉后得到的种群
:param Pm: 变异概率默认是0.01
:return: 经变异操作后的新种群
"""
updatepopulation = np.copy(population)
m, n = population.shape
gene_num = np.uint8(m * n * Pm)
mutationGeneIndex = random.sample(range(0, m * n), gene_num)
for gene in mutationGeneIndex:
chromosomeIndex = gene // n
geneIndex = gene % n
if updatepopulation[chromosomeIndex, geneIndex] == 0:
updatepopulation[chromosomeIndex, geneIndex] = 1
else:
updatepopulation[chromosomeIndex, geneIndex] = 0
return updatepopulation
def fitnessFunction():
return lambda x: 21.5 + x[0] * np.sin(4 * np.pi * x[0]) + x[1] * np.sin(20 * np.pi * x[1])
def main(max_iter=500):
optimalSolutions = []
optimalValues = []
decisionVariables = [[-3.0, 12.1], [4.1, 5.8]]
lengthEncode = getEncodedLength(boundarylist=decisionVariables)
chromosomesEncoded = getIntialPopulation(lengthEncode, 10)
for iteration in range(max_iter):
decoded = decodedChromosome(lengthEncode, chromosomesEncoded, decisionVariables)
evalvalues, cum_proba = getFitnessValue(fitnessFunction(), decoded)
newpopulations = selectNewPopulation(chromosomesEncoded, cum_proba)
crossoverpopulation = crossover(newpopulations)
mutationpopulation = mutation(crossoverpopulation)
final_decoded = decodedChromosome(lengthEncode, mutationpopulation, decisionVariables)
fitnessvalues, cum_individual_proba = getFitnessValue(fitnessFunction(), final_decoded)
optimalValues.append(np.max(list(fitnessvalues)))
index = np.where(fitnessvalues == max(list(fitnessvalues)))
optimalSolutions.append(final_decoded[index[0][0], :])
chromosomesEncoded = mutationpopulation
optimalValue = np.max(optimalValues)
optimalIndex = np.where(optimalValues == optimalValue)
optimalSolution = optimalSolutions[optimalIndex[0][0]]
return optimalSolution, optimalValue
solution, value = main()
print('最优解: x1, x2')
print(solution[0], solution[1])
print('最优目标函数值:', value)
elapsedtime = timeit.timeit(stmt=main, number=1)
print('Searching Time Elapsed:(S)', elapsedtime)
|